Elbow Arthroscopy
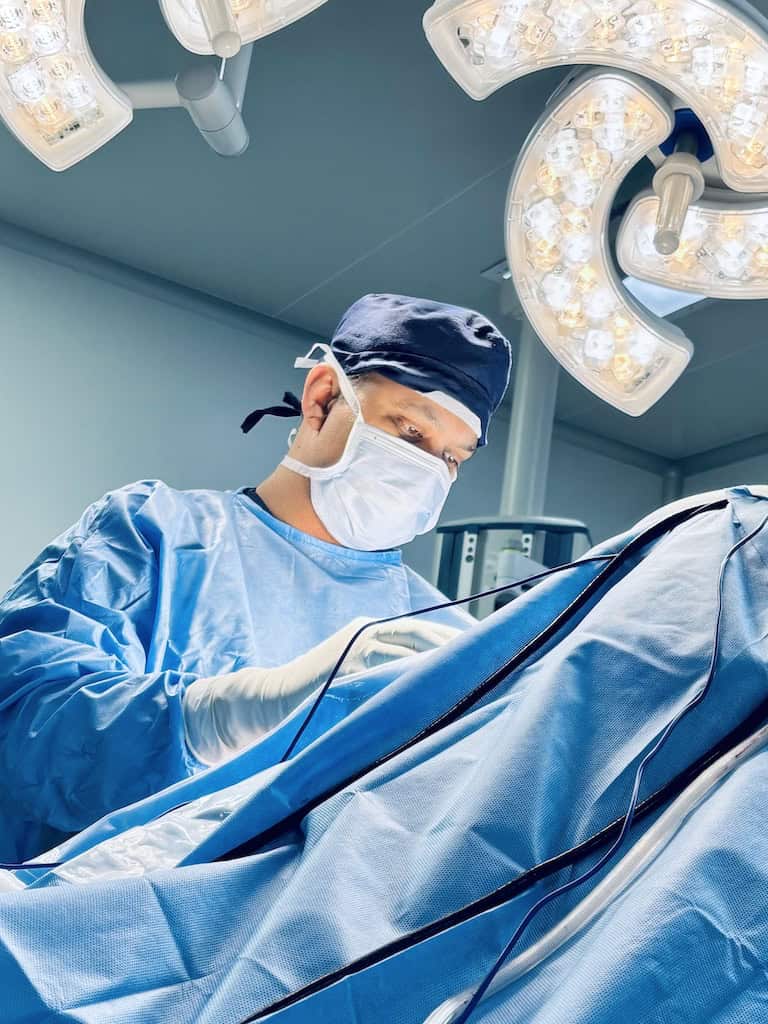
Elbow arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat various elbow joint problems. It involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) into the elbow joint through small incisions to visualize, diagnose, and treat conditions without the need for a large open incision.
Elbow arthroscopy is performed using an arthroscope—a pencil-thin instrument with a camera and light—inserted into the joint. This allows the surgeon to see the inside of the elbow and guide small surgical tools through additional tiny incisions to perform repairs.
It has got advantages over open surgery such as smaller incisions, less tissue damage, reduced pain and scarring, and aster recovery.
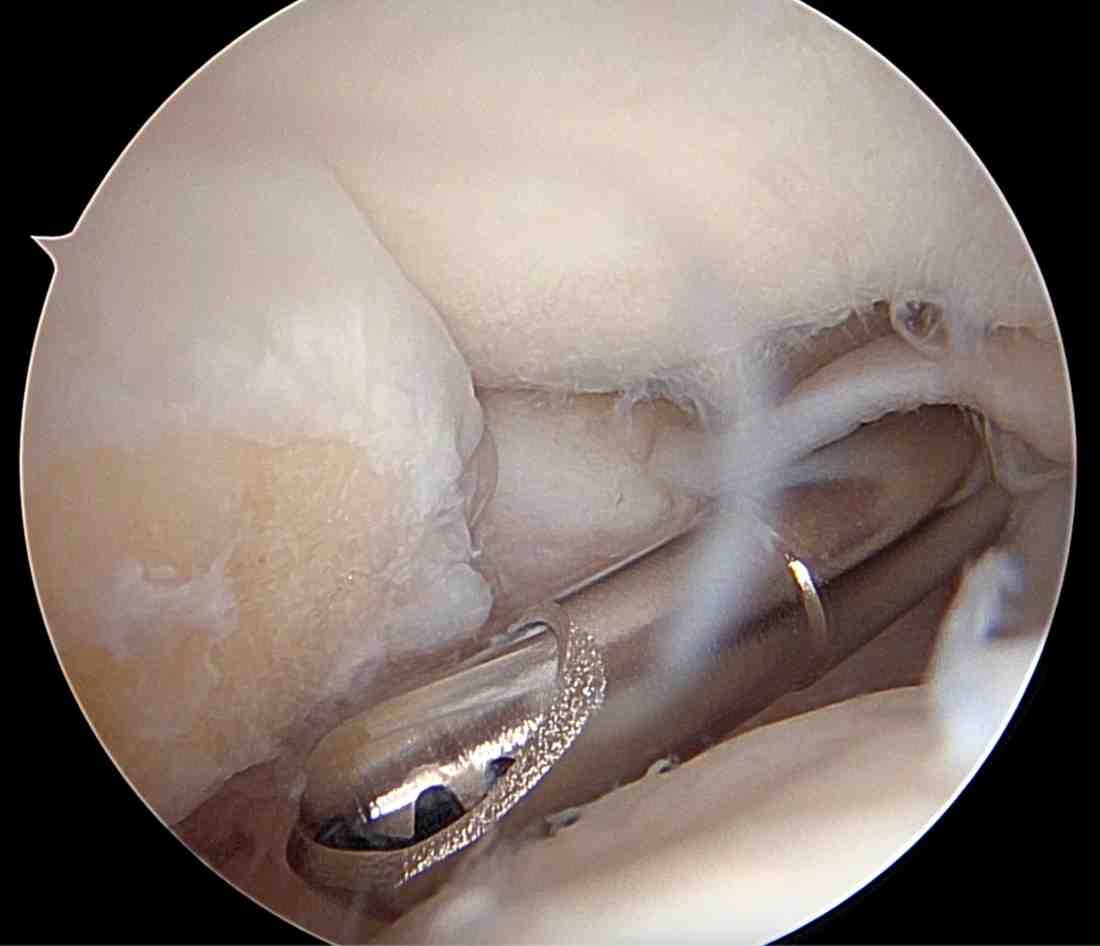
Indications for Elbow Arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy is typically used when conservative treatments (medication, physical therapy, injections) have failed. Common conditions treated with elbow arthroscopy include:
Diagnostic Purposes:
- Unexplained elbow pain
- Joint locking or catching
- Evaluation of cartilage or ligament injuries
Therapeutic Purposes:
| · Loose bodies (cartilage or bone fragments) – Removal to improve motion and reduce pain | |
| · Osteoarthritis or post-traumatic arthritis – Debridement (removal of bone spurs and damaged tissue) | |
| · Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) – Release of the extensor tendon origin | |
| · Synovitis (inflammatory arthritis) – Synovectomy (removal of inflamed tissue) | |
| · Elbow stiffness/contracture – Capsular release to improve motion | |
| · Osteochondritis dissecans – Debridement or microfracture technique | |
| · Elbow fractures – Occasionally used for fragment removal or fixation assistance |
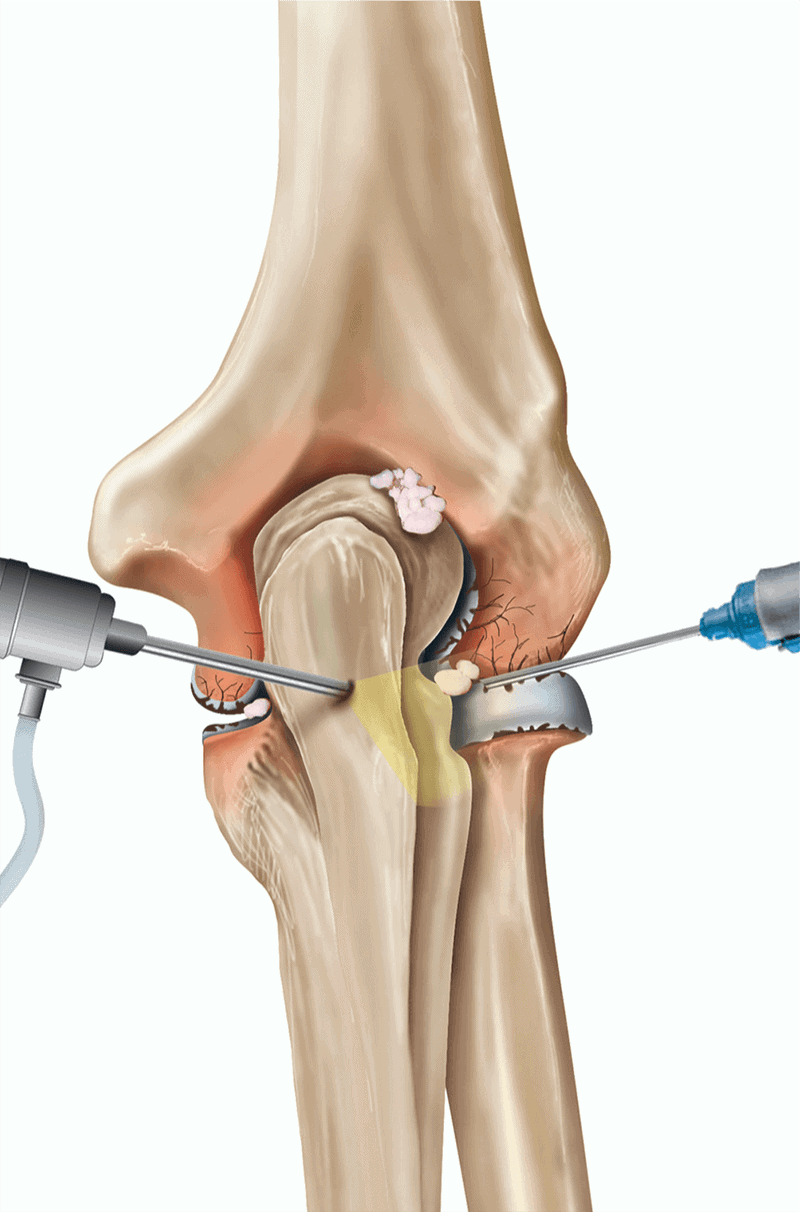
Clinical Pathway
- You will be seen by the specialist in outpatient department for clinical evaluation.
- You will be asked certain questions related to your symptoms and examined thoroughly.
- Your investigations such as X-ray, CT, MRI will be reviewed, following which a surgical plan of surgery will be made.
- A detailed explanation will be given to you with regards to surgery along with its pros and cons.
- You will be seen by the anesthetic team
- Your fitness for surgery will be evaluated.
- Investigations including blood tests will be carried out.
- A physical therapist will explain you with regarding to the post op precautions, exercises and immobilization.
- You will be admitted on the day of surgery in the morning. The surgery will be performed under general and regional anesthesia.
- After surgery, you will be under certain medication to control your post operative pain to make you comfortable.
- You will be discharged in next two to three days with post operative instructions.
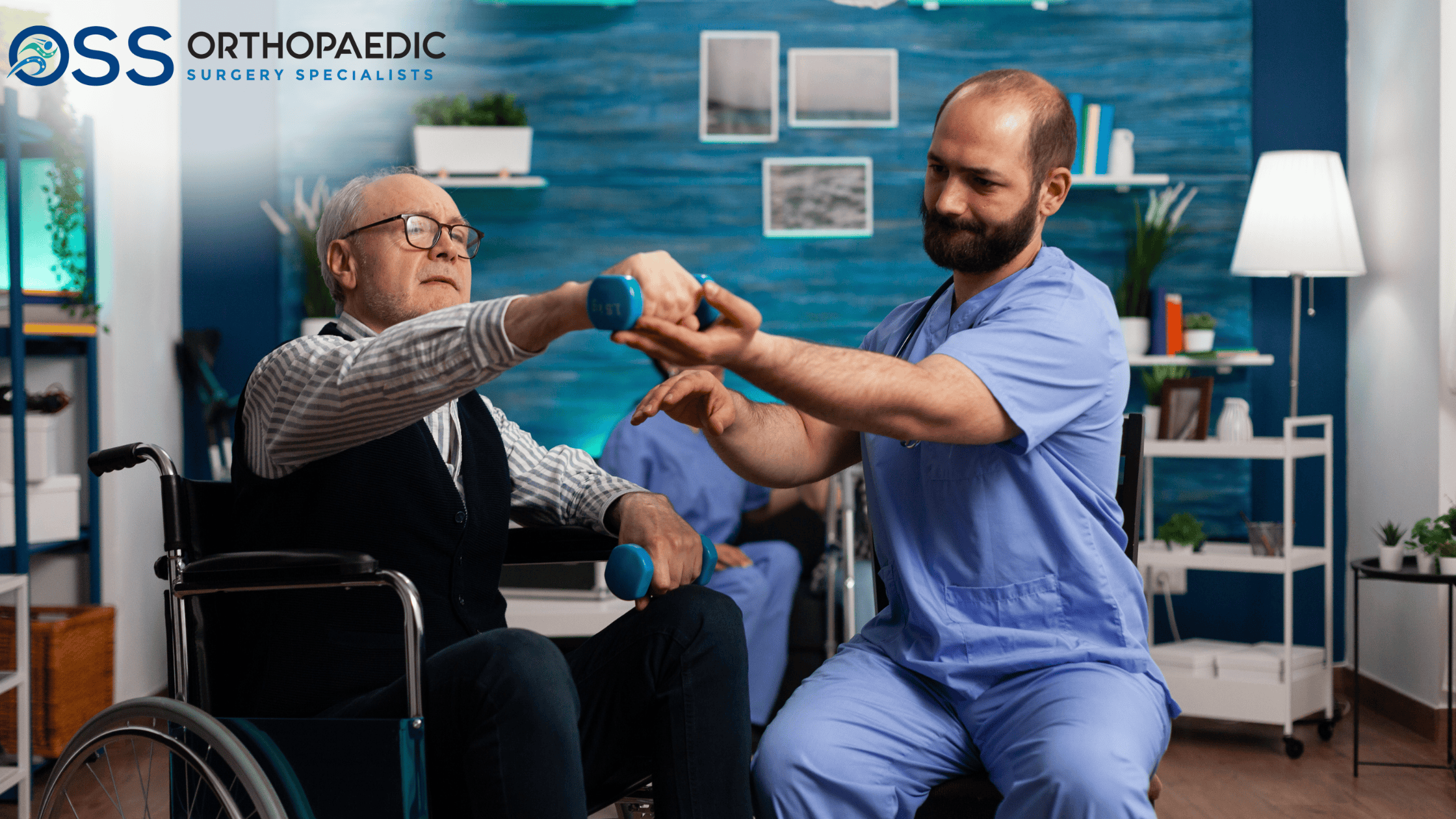
- Your physical therapy will be started on the next day after surgery and will continue for around three months.
- You will be required to see the specialist in outpatient clinic on couple of occasions to assess the recovery. You were expected to recover completely in approximately three to six months.
To summarise, elbow arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used for pain, stiffness, arthritis, loose bodies, tendon issues and causes Less pain, faster recovery, smaller scars than open surgeries, with high success rate when performed for appropriate conditions.