Shoulder Arthroscopy
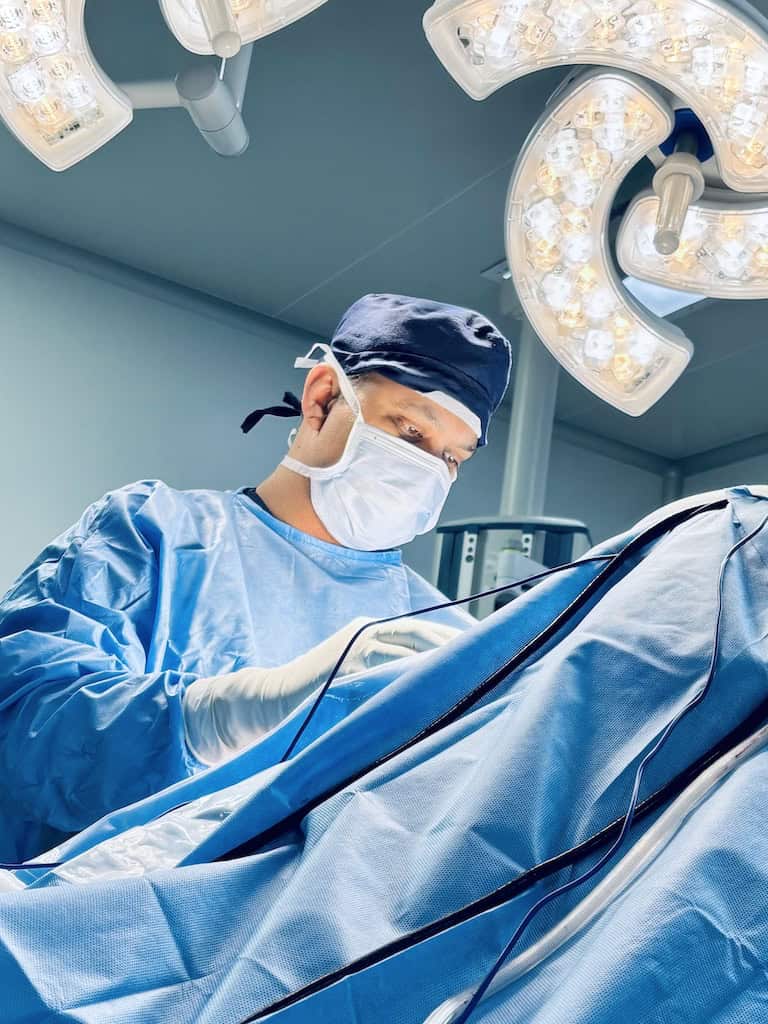
Shoulder arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems within the shoulder joint. It involves the use of a small camera called an arthroscope, inserted through tiny incisions. This allows orthopaedic surgeons to visualize, diagnose, and repair a wide range of shoulder conditions with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues. It has got advantages over open surgery such as smaller incisions, less scarring, reduced post-op pain and swelling, shorter recovery time, lower risk of infection, better cosmetic result, earlier return to activities (depending on the procedure).
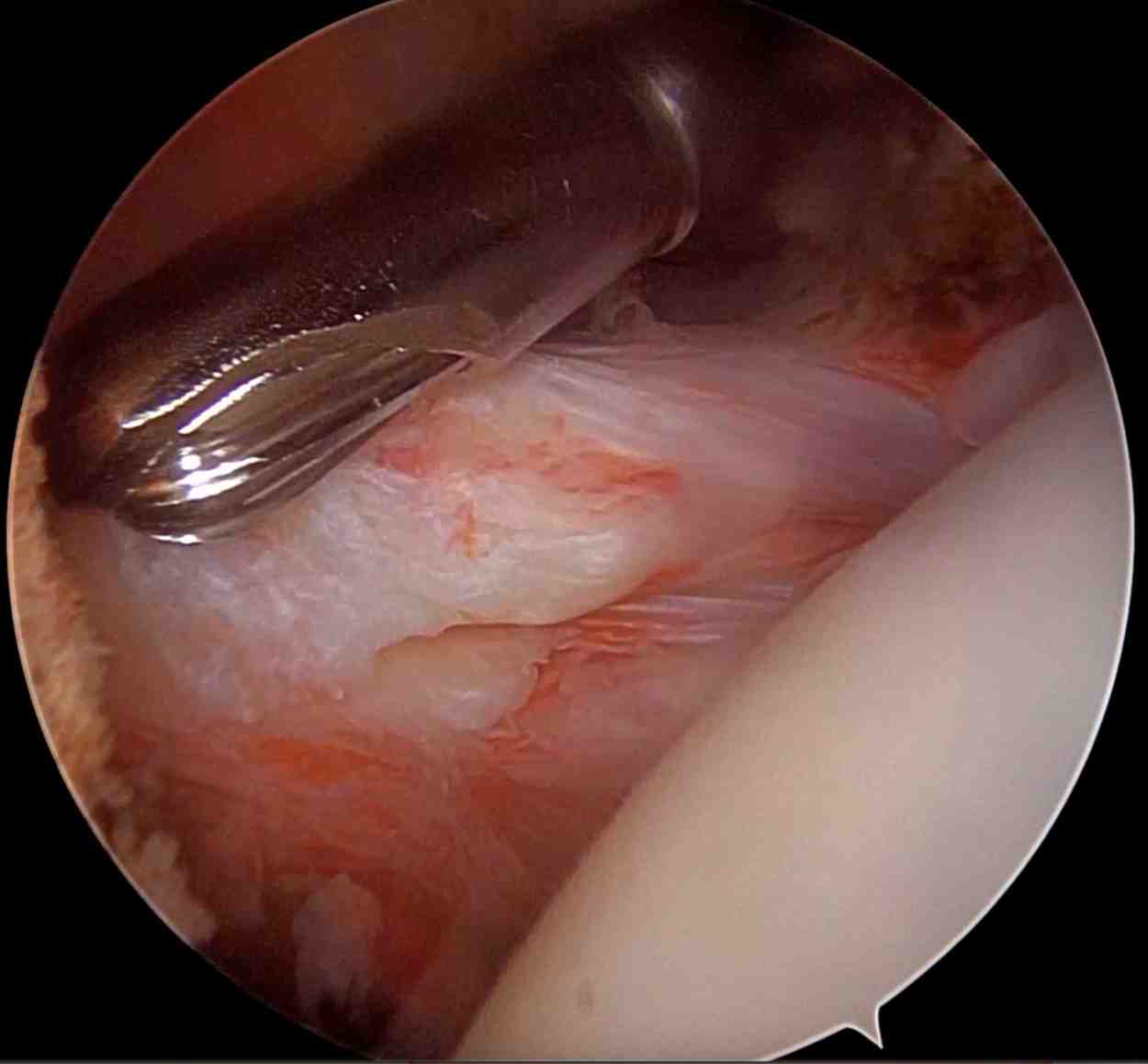
Indications for Shoulder Arthroscopy
Shoulder arthroscopy is commonly recommended for patients with persistent shoulder pain, dysfunction, or instability that has not responded to conservative treatments (e.g., physical therapy, medications, injections).
Common Conditions Treated
- Rotator Cuff Tears – Partial or complete tearing of the tendons.
- Labral Tears (e.g., SLAP or Bankart lesions) – Often related to shoulder dislocations or overhead sports.
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome – Inflammation or bone spurs that compress soft tissues.
- Shoulder Instability – Recurrent dislocations due to ligament or labrum damage.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis) – In some cases, release is done arthroscopically.
- AC Joint Arthritis – Resected arthroscopically for pain relief.
- Loose Bodies or Cartilage Damage – Clean-up or debridement of the joint.
- Biceps Tendon Disorders – Such as biceps tenotomy or tenodesis.
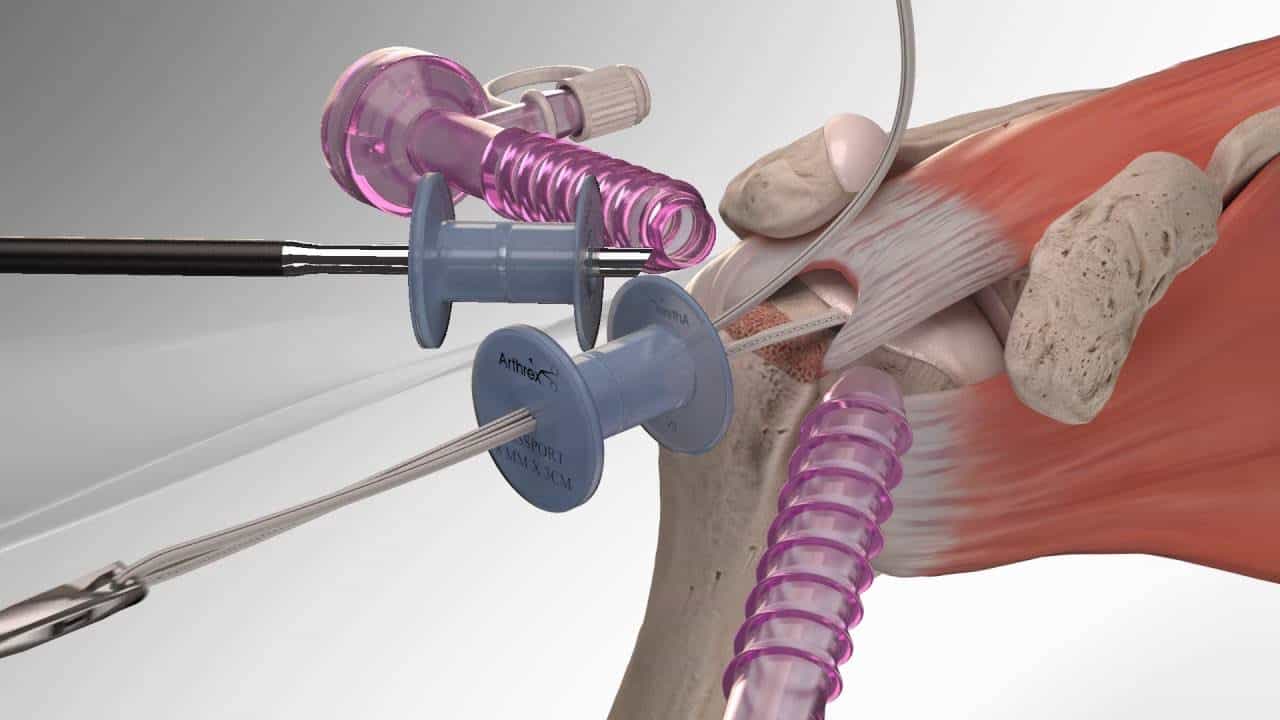
Clinical Pathway
- You will be seen by the specialist in outpatient department for clinical evaluation.
- You will be asked certain questions related to your symptoms and examined thoroughly.
- Your investigations such as X-ray, MRI will be reviewed, following which a surgical plan of surgery will be made.
- A detailed explanation will be given to you with regards to surgery along with its pros and cons.
- You will be seen by the anesthetic team
- Your fitness for surgery will be evaluated.
- Investigations including blood tests will be carried out.
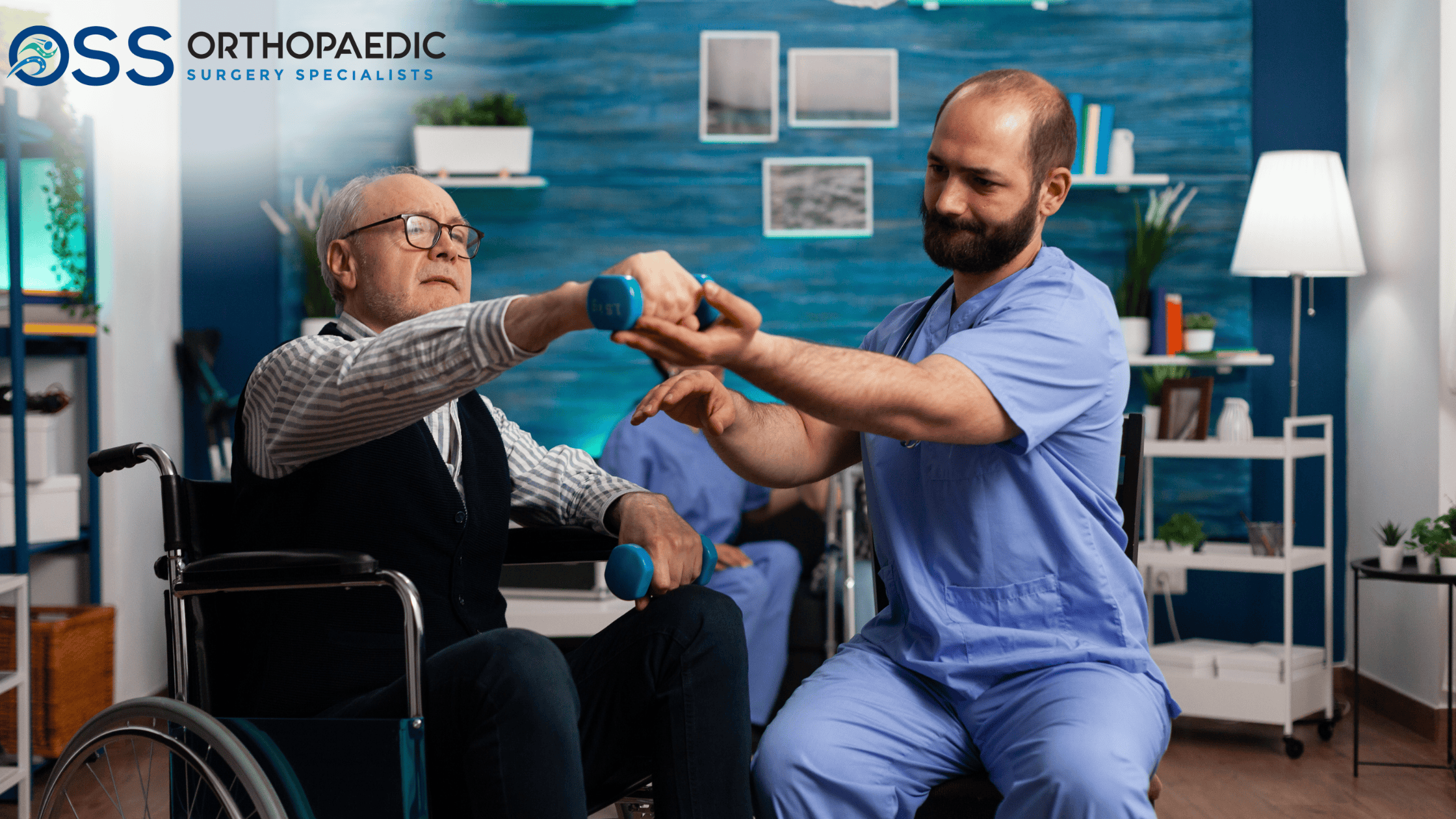
- A physical therapist will explain you with regarding to the post op precautions, exercises and immobilization.
- You will be admitted on the day of surgery in the morning. The surgery will be performed under general and regional anesthesia.
- After surgery, you will be under certain medication to control your post operative pain to make you comfortable.
- You will be discharged the next day with post operative instructions.
- Your physical therapy will be started on the next day after surgery and will continue for around three months.
- You will be required to see the specialist in outpatient clinic on couple of occasions to assess the recovery. You were expected to recover completely in approximately three to six months.