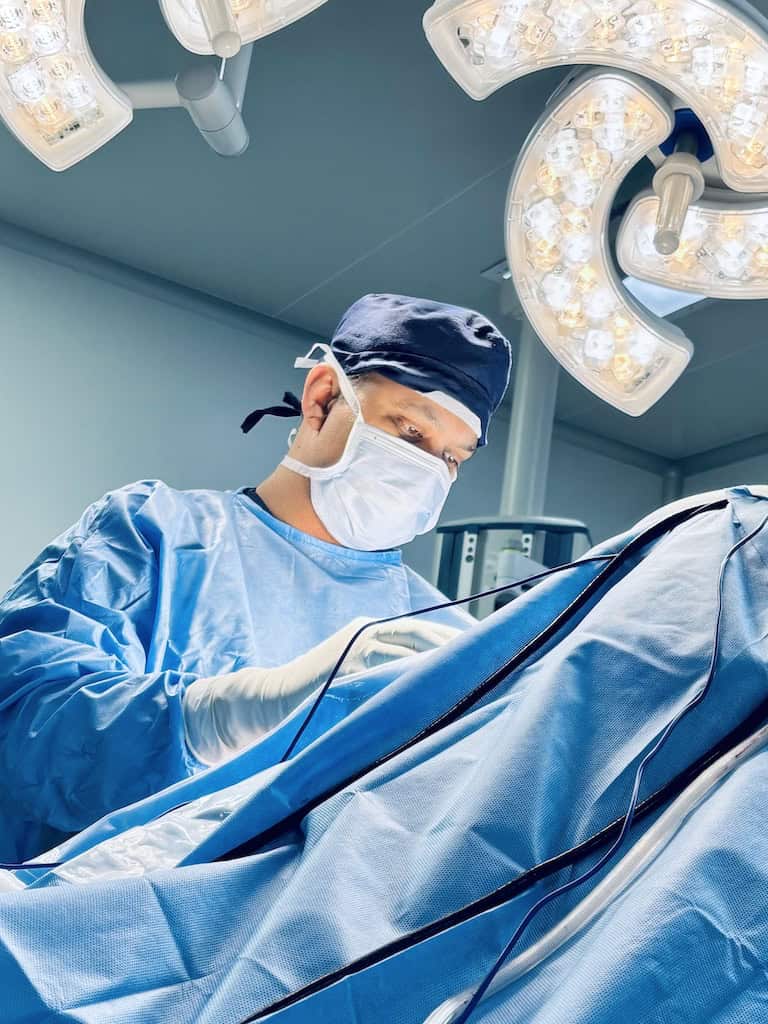
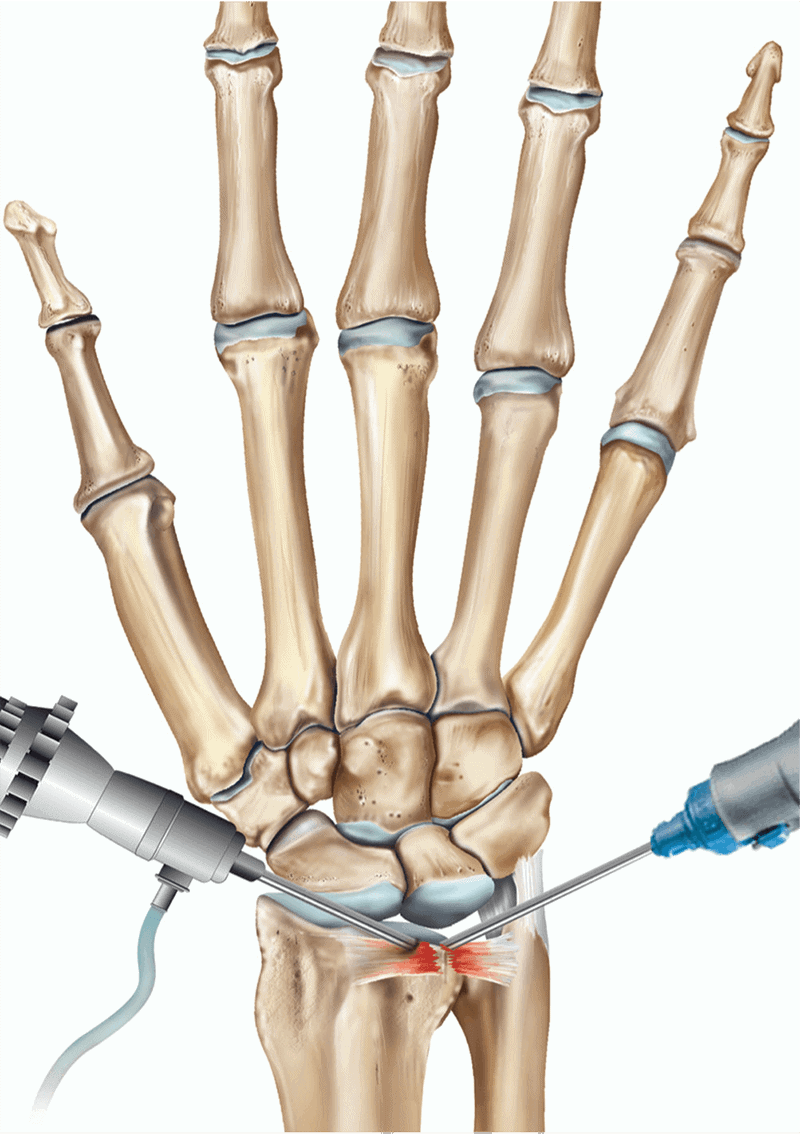
Wrist Arthroscopy
Wrist arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows direct visualization, diagnosis, and treatment of wrist joint pathologies using a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments. Since the wrist is a complex joint with multiple small bones, ligaments, and cartilage structures, arthroscopy provides a precise and less traumatic way to address conditions that previously required open surgery.
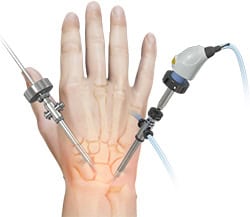
Indications for Wrist Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Diagnostic Indications:
- Unexplained chronic wrist pain
- Suspected TFCC tear
- Suspected ligament injury (scapholunate, lunotriquetral)
- Early cartilage lesions
- Assessment before reconstructive surgery
Therapeutic Indications:
- TFCC repair or debridement
- Ligament repair/reconstruction (e.g., scapholunate ligament)
- Removal of loose bodies or synovectomy
- Carpal bone fractures (reduction and fixation)
- Ganglion cyst excision
- Wrist arthrodesis (partial fusion)
- Management of intra-articular distal radius fractures
Clinical Pathway
- You will be seen by the specialist in outpatient department for clinical evaluation.
- You will be asked certain questions related to your symptoms and examined thoroughly.
- Your investigations such as X-ray and MRI will be reviewed, following which a surgical plan of shoulder replacement will be made.
- A detailed explanation will be given to you with regards to surgery along with its pros and cons.
- You will be seen by the anesthetic team
- Your fitness for surgery will be evaluated.
- Investigations including blood tests will be carried out.
- A physical therapist will explain you with regarding to the post op precautions, exercises and immobilization.
- You will be admitted on the day of surgery in the morning. The surgery will be performed under general anesthesia.
- You may be given a plaster for few weeks depending on the nature of intervention.
- After surgery, you will be under certain medication to control your post operative pain to make you comfortable.
- You will be discharged the next day with post operative instructions.
- You will be required to see the specialist in outpatient clinic on couple of occasions to assess the recovery. You were expected to recover completely in approximately three to six months.